Search engines use crawlers to find new and updated content. Content can range from web pages to PDF files and images. What all content have in common, however, is that they're discovered via links.
The most important crawler is Googlebot, Google's crawler, because more than 90% of searches are performed via Google. It works by visiting web pages on its index and then following the links within those pages to find new pages. Thus, Googlebot can discover new and updated content by following links, which is why backlinks are still a key ranking factor.
Clicks and Rankings
When you search on Google, Google will check its index for relevant content and rank it to answer your query. In theory, the highest-ranked result will be the best and most relevant to your query. However, in practice, that's often not the case.
Our SEO analyst set out to establish how Googlebot crawls affect page ranking and the dependency between crawl frequency and URL performance. Here is what they discovered.
The Study Dataset
The analysis is based on a UK-based website's actual data with average monthly organic search impressions of 1.2M and 3.5k indexed pages.
For this analysis, the team combined data from Googlebot crawl events (GET requests from google.com/bot) and Google Search Console's daily URL performance for a period of 15 days in September 2020.
For each URL, they calculated the number of crawls per day. Then, the frequency of crawls for each URL was calculated by dividing 15 (the total number of days) by the number of days on which there was at least one crawl.
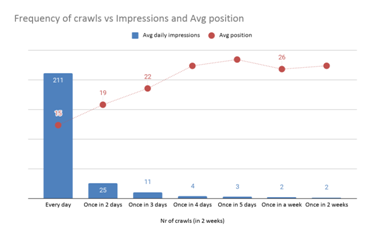
Predictably, the more frequent the crawls, the higher the number of daily impressions and clicks were. The ranking of these pages was also higher.
In this study, the number of URLs crawled every day was 81, which had 211 daily impressions and 3.59 clicks on average, and an average position of 15. Meanwhile, 1866 URLs were crawled once every two weeks, which had 2 daily impressions, 0.01 clicks, and an average position of 27.
Average Crawl Frequency (Once In) | Nr Of Urls | Avg Daily Impressions | Avg Daily Clicks | Avg Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Everyday | 81 | 211 | 3.59 | 15 |
Once in 2 days | 540 | 25 | 0.42 | 19 |
Once in 3 days | 162 | 11 | 0.08 | 22 |
Once in 4 days | 343 | 4 | 0.02 | 27 |
Once in 5 days | 677 | 3 | 0.02 | 28 |
Once in a week | 1068 | 2 | 0.02 | 26 |
Once in 2 weeks | 1866 | 2 | 0.01 | 27 |
Introducing Pearson’s Coefficient of Linear Correlation
You'll agree that with age, children tend to get taller. A statistician would say there was a very strong positive relationship between age and height. The Pearson coefficient of correlation would range from 0.70 to 1, depending on the study sample.
Likewise, the higher the speed of a car, the shorter the traveling time; if you drive faster, you'll arrive at your destination sooner. We then speak of a very strong negative relationship between speed and travel time. In this case, the coefficient would range from -0.70 to -1.
The team calculated the Pearson correlation coefficient between the number of days with crawls and the average daily impressions, a metric quantifying how many times a page is displayed on the search engine results pages (SERPs). The coefficient between the number of crawls, clicks, and position (ranking) was calculated too.
Header | Nr Of Crawls |
|---|---|
Avg impressions | 0.69 |
Daily clicks | 0.66 |
Position | -0.69 |
The coefficient between the number of crawls and average impressions was 0.69, which shows a strong positive relationship between them. It was 0.66 between the number of crawls and the clicks per day and -0.69 between the number of crawls and the position of the URL. This last negative value shows that high URL crawling frequency is associated with a low average position number. In this case, this means more often crawled URLs are closer to the top SERP position.
The team compared two types of URLs: high-ranking URLs with low impressions (average position 1-5 and average daily number of impressions <=5) and low-ranking URLs with high impressions (position >20 and daily number of impressions >=50). They found low-ranking URLs with more impressions were crawled almost twice as often: 8.7 vs. 4.6. This led them to conclude impressions were a more important factor for crawl frequency.
How are Crawl Frequency and Page Ranking Connected?
To determine how Googlebot affects page ranking in the days after a crawl, the analyst combined data from three sources: a list of crawls and their frequency for a period of two weeks in September 2020 and the avg daily position of each keyword and the corresponding URL.
They noted the position of each keyword and URL;
- on the day before the last crawl
- on the day of the crawl
- and each day for five days after the crawl
They filtered out URLs that were crawled more frequently than once every three days because these could have been affected by previous crawls, potentially resulting in data inaccuracy. They also filtered out keywords that had no position data on the day before the crawl.
Position Change | Avg Dtd Change | Day Of Last Crawl | 1 Day After Last Crawl | 2 Day After Last Crawl | 3 Day After Last Crawl | 4 Day After Last Crawl | 5 Day After Last Crawl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Avg DtD change | 1.1 | 1.6 | 3.5 | 2.2 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.6 |
Avg % DtD change | 3.71% | 5% | 6% | 4% | 3% | 1% | 3% |
Avg change to the day before crawl | Cell | 1.6 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 3.2 | 2.4 | 2.9 |
Avg %change to the day before crawl | Cell | 5% | 8% | 11% | 11% | 8% | 10% |
The share of URLs with position improvement after the crawl was 64%. The position was higher than before the crawl on the third day after it. The share of URLs, whose position deteriorated after the crawl, was 36%.
High-ranking URLs were less volatile. For first, second, and third-ranked URLs, the average day-to-day change was just 0.13 compared to 2.08 for URLs ranking 21st or lower.
Avg Dtd Change In Position Depending On Avg Position | Avg Dtd Change |
|---|---|
Avg position 1-3 | 0.13 |
Avg position 4-10 | 0.15 |
Avg position 11-20 | 0.64 |
Avg position >21 | 2.06 |
What do These Findings Mean?
If your site isn't crawled and indexed, it won't appear on the SERPs. That is the only thing that is obvious. We have seen a correlation between crawl frequency and page impressions, as well as crawl and page ranking movements.
However, based on our understanding of how Google's algorithm works, the page ranking movement in relation to crawl is most probably due Google's re-calibration of the page's ranking after they've crawled it and re-calculated its 'relevancy score'. Since page impressions is directly tied to rankings, that is also directly impacted by that crawl.
Our advice is to check how many of your pages are indexed on your site and whether Google is crawling and locating all of the pages that need to be crawled or is it wasting the crawl budget on URLs that shouldn't be crawled. This is generally only an issue with very large websites.
To check if all of the important pages have been indexed, you can check Google Search Console > Coverage.
You can help to prioritize URL's crawl rate by increasing the quantity and quality of internal and external links pointing to it. You can also ensure that you are not wasting crawl budget on low-priority pages by decreasing the number of internal links pointing to them, make those links nofollow, or by adding a disallow crawl instruction on robots.txt file for these URLs.
These will point Googlebot in the right direction in terms of crawling your web content, which will increase your control over what ultimately appears in the index.

